Architecture Design
- Home
- Our Services
- Architecture Design
Architecture Design
Architecture design encompasses the process of creating and planning the layout, form, and functionality of buildings and structures. It involves combining artistic, aesthetic, and technical considerations to produce a well-designed and functional space.
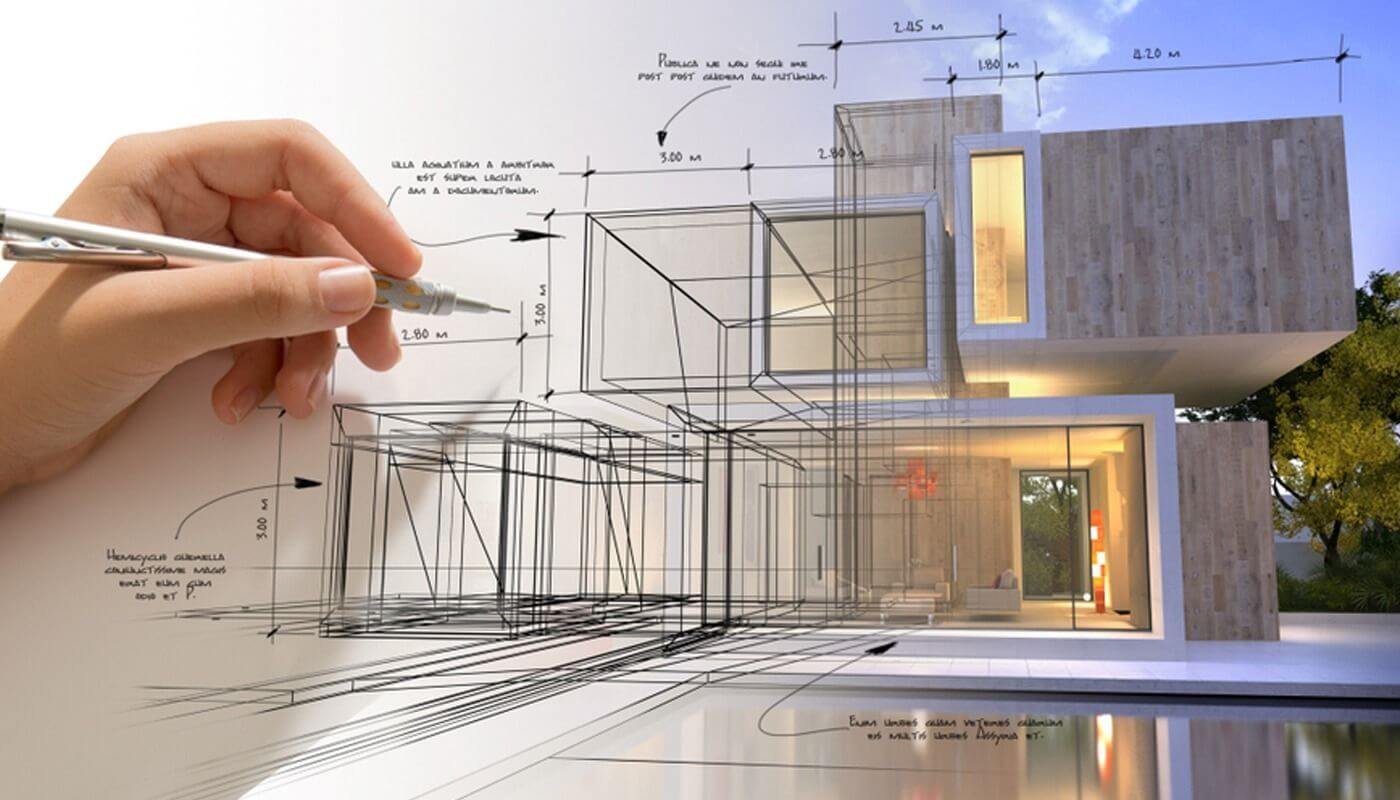
Here are some key aspects of architecture design:
1. Functionality: Architects consider the purpose and requirements of the building or structure they are designing. They analyses the intended use of the space and ensure that it meets the functional needs of its occupants. This includes factors such as spatial organization, circulation, and accessibility.
2. Aesthetics: Architecture design involves creating visually appealing and harmonious spaces. Architects consider elements such as proportions, scale, materials, colours, and textures to create a pleasing aesthetic that aligns with the project’s goals and the surrounding environment.
3. Sustainability: With increasing environmental concerns, sustainable design practices have become crucial in architecture. Architects incorporate strategies to minimize the environmental impact of buildings, such as energy-efficient systems, use of sustainable materials, passive design techniques, and incorporating renewable energy sources.
4. Safety and Building Codes: Architects must adhere to safety regulations and building codes while designing structures. They ensure that the design meets fire safety standards, accessibility guidelines, structural stability requirements, and other relevant codes and regulations.
5. Site Analysis: Before starting the design process, architects conduct a thorough analysis of the site. They consider factors such as topography, climate, vegetation, views, and surrounding context to inform their design decisions and integrate the building harmoniously into its environment.
6. Collaboration: Architects often work closely with clients, engineers, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. Collaboration and effective communication are essential to ensure that the design intent is properly translated into the final built form.
7. Technology: Architecture design has been significantly influenced by technological advancements. Computer-aided design (CAD) software allows architects to create detailed 2D and 3D models, facilitating visualization and coordination with other disciplines. Additionally, Building Information Modeling (BIM) software enables architects to create digital representations of the building, enhancing coordination and information exchange among project stakeholders.


Architecture Design Types
Architecture design encompasses a wide range of types, styles, and approaches. Here are some common types of architecture design:
1. Residential Architecture: This type focuses on designing homes, apartments, and other residential structures. It includes various styles like modern, contemporary, traditional, and more.
2. Commercial Architecture: Commercial architecture involves designing structures for commercial purposes, such as office buildings, shopping malls, hotels, restaurants, and retail spaces. It often requires considering factors like functionality, branding, and customer experience.
3. Industrial Architecture: Industrial architecture deals with designing buildings and structures for industrial purposes, such as factories, warehouses, power plants, and manufacturing facilities. It emphasizes efficient space utilization, workflow optimization, and safety considerations.
4. Institutional Architecture: Institutional architecture involves designing structures for institutions like schools, universities, hospitals, museums, libraries, government buildings, and religious buildings. It often requires considerations for specific needs, regulations, and the overall purpose of the institution.
5. Landscape Architecture: Landscape architecture focuses on designing outdoor spaces, including parks, gardens, public plazas, and recreational areas. It incorporates elements like landform manipulation, plant selection, hardscape design, and environmental sustainability.
6. Interior Architecture: Interior architecture is concerned with the design and arrangement of interior spaces within buildings. It includes aspects like spatial planning, material selection, lighting, furniture, and other elements to create functional and aesthetically pleasing interiors.
7. Sustainable Architecture: Sustainable architecture emphasizes environmentally friendly design practices, aiming to minimize the negative impact on the environment and maximize energy efficiency. It incorporates strategies like passive design, renewable energy systems, efficient use of resources, and sustainable materials.
8. Adaptive Reuse Architecture: Adaptive reuse architecture involves repurposing existing buildings or structures for new functions while retaining their historic or architectural value. It often requires creative problem-solving to adapt the space to its new purpose while preserving its character.
9. Vernacular Architecture: Vernacular architecture refers to traditional or indigenous architectural styles and techniques that are specific to a particular region or culture. It reflects the local climate, materials, and cultural practices, often incorporating sustainable design principles.
10. Parametric Architecture: Parametric architecture utilizes computational design tools and algorithms to create complex and highly customizable forms. It involves the use of parametric modeling software to generate designs that respond to specific parameters or constraints.







